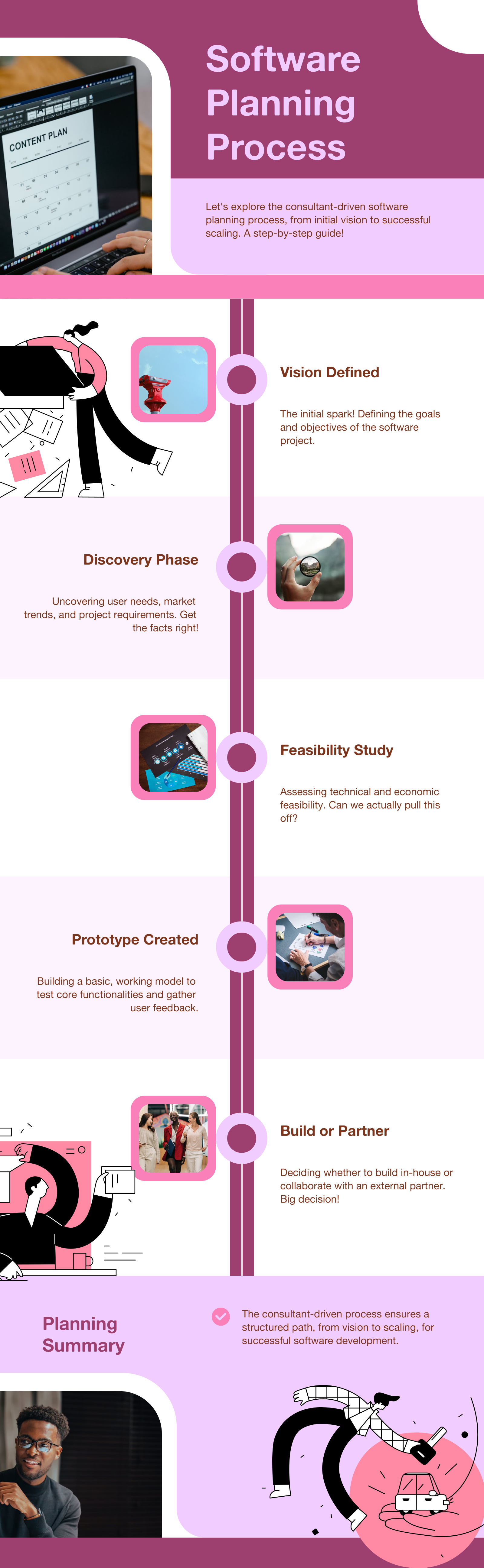
SaaS Development Process in 2025: Step-by-Step Guide from Idea to Launch

SaaS Development Process: Complete Guide to Building a Scalable SaaS Product in 2025
Introduction
The global SaaS market is projected to surpass $300 billion by 2026, and every year, more businesses are moving from traditional software to cloud-based solutions.
But here’s the catch — while SaaS products look simple from the outside, the SaaS development process is a highly structured journey that requires deep planning, technical execution, market alignment, and continuous improvement.
In this guide, you’ll discover every stage of building a SaaS product in 2025 — from validating your idea to designing architecture that can handle millions of users.
Whether you’re a startup founder, CTO, or entrepreneur, this process will help you reduce development risks, optimize costs, and launch faster.
Understanding the SaaS Development Process
Before diving into the steps, it’s important to define what makes SaaS development unique compared to other software development approaches:
Cloud-Hosted — No installation on user devices, accessed via browsers or apps.
Subscription Model — Revenue comes from recurring payments.
Scalable Architecture — Built to handle thousands or millions of simultaneous users.
Continuous Delivery — Updates are rolled out instantly to all customers.
Data-Driven Decision Making — Built-in analytics to guide product improvements.
Tip: People might ask,
“What is the SaaS development process?” or “How do you build a SaaS product?”
That’s why we’ve framed our content with conversational subheadings and direct, actionable answers.
Stage 1 – Market Research & Idea Validation
You cannot afford to build first and validate later. The SaaS market is crowded, and 90% of SaaS startups fail because they skip proper validation.
Step 1: Identify a Problem Worth Solving
Talk to real users in your target industry.
Analyze existing SaaS solutions — what do users love, and where are they frustrated?
Look for inefficiencies you can automate or optimize.
Example: Slack succeeded because it replaced slow, email-heavy communication with a faster, centralized chat platform for teams.
Step 2: Competitive Analysis
Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and G2 to analyze competitors.
Identify feature gaps you can capitalize on.
Check pricing models, UI/UX design trends, and brand positioning.
Step 3: Define Your Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
Your UVP should answer the question:
“Why would someone switch to your SaaS product?”
Pro Tip: If your UVP can’t be explained in one sentence, it’s not clear enough.
Stage 2 – Defining SaaS Requirements & Business Goals
Once you have validated your idea, it’s time to document your product requirements and set measurable goals.
Business Goals
Revenue Targets (e.g., $50K MRR in 12 months)
Market Penetration (e.g., capture 5% of the SMB accounting software market)
User Growth Rate (e.g., grow from 0 to 5,000 active users in 6 months)
Functional Requirements
User authentication & account management
Data security & compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2)
Payment processing (Stripe, PayPal, Razorpay)
Multi-device accessibility
Tip: Many people search for
“What features should my SaaS have?”
We answer this clearly within the content so search engines connect it to intent-based queries.
Stage 3 – Choosing the SaaS Architecture
Your architecture defines how scalable, secure, and fast your SaaS will be.
Key Architectural Decisions
Monolithic vs Microservices — Microservices are preferred for scalability.
Cloud Provider — AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure.
Database — Relational (PostgreSQL, MySQL) vs NoSQL (MongoDB).
Multi-Tenancy — Allows multiple customers to share the same infrastructure securely.
Pro Insight:
Choosing multi-tenant architecture can significantly reduce hosting costs and speed up deployment for new clients.
Stage 4 – UI/UX Design Phase
A SaaS product is not just about functionality — user experience is the growth engine.
Why Design Matters
First Impressions Drive Retention — 38% of users will stop using an app if they find the UI unattractive.
Faster Onboarding = Lower Churn — A well-designed onboarding flow reduces cancellations.
Design Best Practices
Keep navigation minimal and intuitive.
Use color psychology to evoke trust and action.
Create responsive designs for mobile, tablet, and desktop.
Test multiple onboarding variations to find what works best.
Example: Notion’s minimalist UI with contextual help has been a major reason for its adoption.
Stage 5 – Building the MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
An MVP allows you to launch quickly and inexpensively, gathering feedback before full-scale development.
Steps to Build a SaaS MVP
Prioritize core features only (don’t build advanced analytics in v1).
Develop with agile methodology — sprint cycles of 1-2 weeks.
Use CI/CD pipelines for faster deployment.
Test with a small group of beta users.
Goal: Achieve Product-Market Fit before investing in advanced features.
7. Testing and Quality Assurance in SaaS Development
Testing is one of the most underestimated but business-critical phases of the SaaS development process. Unlike traditional software, SaaS platforms are continuously accessible to users, meaning even minor bugs can be instantly visible and can damage your reputation.
7.1 Functional Testing
This ensures that all features work exactly as intended. Testers simulate real-world use cases to check:
Core functionality (e.g., login, dashboards, workflows)
Integrations with third-party APIs
User permissions and role-based access
7.2 Performance Testing
Speed and stability are non-negotiable for SaaS. Performance testing checks:
Page load time (Google recommends <2.5 seconds)
Response under peak traffic
Resource usage optimization
Pro Tip: Use tools like JMeter, LoadNinja, or BlazeMeter for scalable performance testing.
7.3 Security Testing
Because SaaS handles sensitive business data, security testing includes:
Penetration testing
Vulnerability scanning
Data encryption verification
Compliance checks (GDPR, HIPAA, ISO)
8. Deployment and Go-Live Strategy
Going live isn’t just about clicking “Deploy.” It’s a carefully planned event that ensures smooth user onboarding and minimal disruption.
8.1 Pre-Launch Checklist
Final QA Pass: Confirm all features and integrations
Server Scaling: Ensure infrastructure can handle initial user load
Disaster Recovery Plan: Prepare for possible failures
8.2 Deployment Models
Blue-Green Deployment: Two environments, switch users to the updated one when stable
Rolling Deployment: Gradual rollout to minimize risk
Pro Tip: For global SaaS platforms, use CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) to reduce latency for international users.
9. Post-Launch Monitoring and Maintenance
The SaaS journey does not end after launch—in fact, it’s just beginning.
9.1 Continuous Monitoring
Track:
Uptime and downtime logs
API health
Real-time error alerts
9.2 Ongoing Security Updates
Cybersecurity threats evolve daily. Apply patches regularly, conduct security audits, and keep all dependencies up-to-date.
9.3 Customer Feedback Loop
Surveys and NPS (Net Promoter Score) collection
In-app feedback widgets
Social listening for brand mentions
10. SaaS Scaling Strategies
Once your SaaS platform is stable, scaling becomes the next big challenge.
10.1 Vertical Scaling
Adding more power to existing servers to handle higher loads.
10.2 Horizontal Scaling
Adding more servers to distribute traffic.
10.3 Multi-Tenancy Optimization
Fine-tuning databases and architecture to serve more customers without performance degradation.
11. Common Mistakes in the SaaS Development Process (and How to Avoid Them)
11.1 Skipping MVP Stage
Skipping the MVP often leads to wasted resources on features users may not need. Always validate with real-world feedback.
11.2 Neglecting Documentation
Clear documentation helps both internal teams and customers. Maintain developer docs, API docs, and user manuals.
11.3 Poor Data Migration Planning
Data transfer from legacy systems must be secure, accurate, and tested before going live.
12. Future Trends in SaaS Development
AI-Driven SaaS: Automated workflows and predictive analytics
Serverless Architecture: Lower infrastructure costs
Low-Code/No-Code Development: Faster MVPs with minimal coding
Hyper-Personalization: Custom dashboards and workflows per user role
13. SaaS Development Process Checklist
✅ Define target audience & market fit
✅ Choose scalable architecture & tech stack
✅ Prioritize security & compliance
✅ Build MVP, gather feedback, iterate
✅ Test thoroughly before launch
✅ Deploy with rollback plan
✅ Monitor, maintain, and scale
14. Conclusion
The SaaS development process is not just a technical workflow—it’s a business growth strategy. By following structured stages, prioritizing user experience, and embracing continuous improvement, your SaaS product can achieve long-term success.
Remember: Speed gets you noticed, quality keeps you in business.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s Build Your SaaS
Ready to transform your SaaS idea into a market-ready platform? YoWill Infotech specializes in scalable, secure, and user-friendly SaaS solutions tailored to your business goals.
📩 Get Your Free SaaS Development Consultation Today
Contact Us